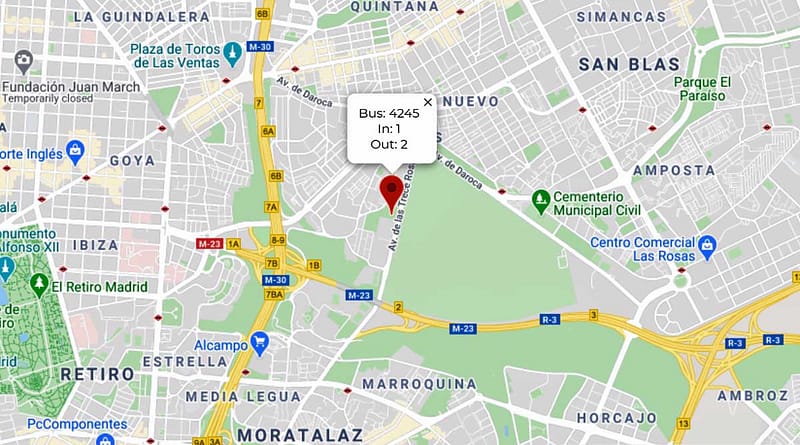
Passenger counters connect to smart bus stops
As the smart city evolves it incorporates sustainability and inclusivity. Among the most vulnerable group of citizens are the elderly, and their mobility around the city is still a major challenge. Smart cities’ technology could be used to maintain their quality of life. Researchers in Madrid have used Retail Sensing passenger counting systems to develop inclusive smart bus stops, making transport services available for everyone.
Led by Professor Victor Manuel Padrón Nápoles, the team used our video-based passenger counters. The cameras, located above the front and rear doors, use artificial vision algorithms to count passengers in and out. This information was sent through a 4G router to an MQTT server to make it globally available.

First the researchers tested the camera system in the Lab. They then installed it inside a bus and tested it during daily operations in the centre of Madrid as they developed their trip planner.
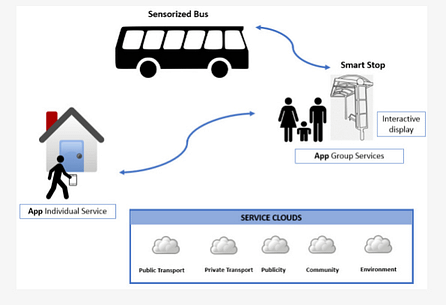
The trip planner includes options for walking, cycling, private and public transport. All data is collected anonymously. The new functionality of the Interconnected Public Space is being developed in the current prototype of a smart bus stop.
Further Reading
Padrón Nápoles, V.; Gachet Páez, D.; Esteban Penelas, J.; García Pérez, O.; García Santacruz, M.; Martín de Pablos, F. Smart bus stops as interconnected public spaces for increasing social inclusiveness and quality of life of elder users. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 430–443.
Automated Passenger Counting, Retail Sensing, accessed 8 September 2020
Smart City Solutions, Retail Sensing, accessed 8 September 2020